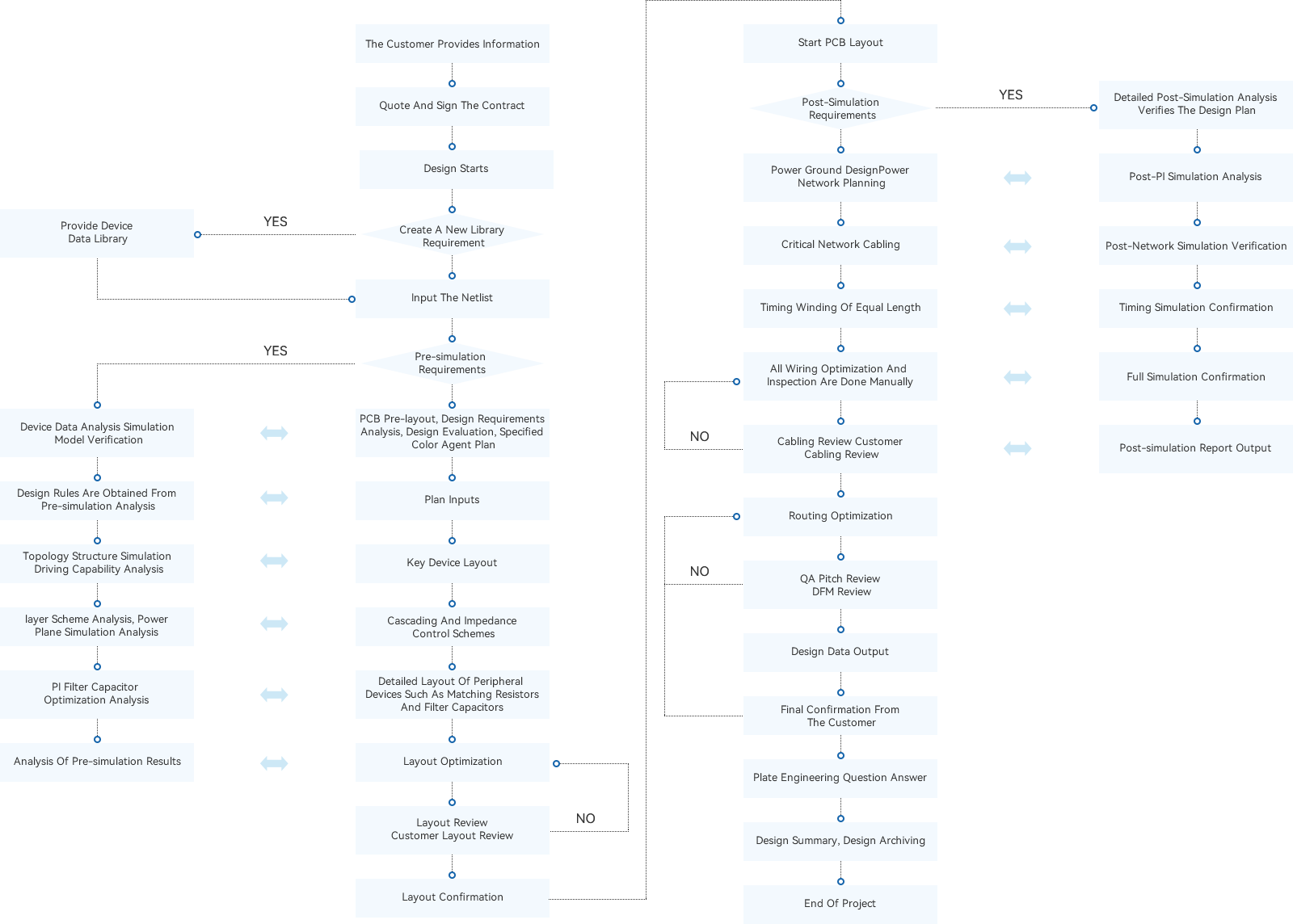
Signal integrity analysis
-
Design rules, topology pre-imitation
-
Reflection, crosstalk, timing analysis
-
Multi-plate joint system analysis
Support IBIS model, Hspice model and S-parameter model frequency domain,time domain, channel multiple simulation analysis methods, to ensure high-speed transmission performance comprehensive consideration of reflection, crosstalk, ringing, eye diagram, jitter, bit error rate, S-parameter DDR3, DDR3L, DDR4, PCIE, Serdes, SFP+ a large number of simulation cases, with rich practical experience